
Draw the Lewis electron structure of the molecule or polyatomic ion.
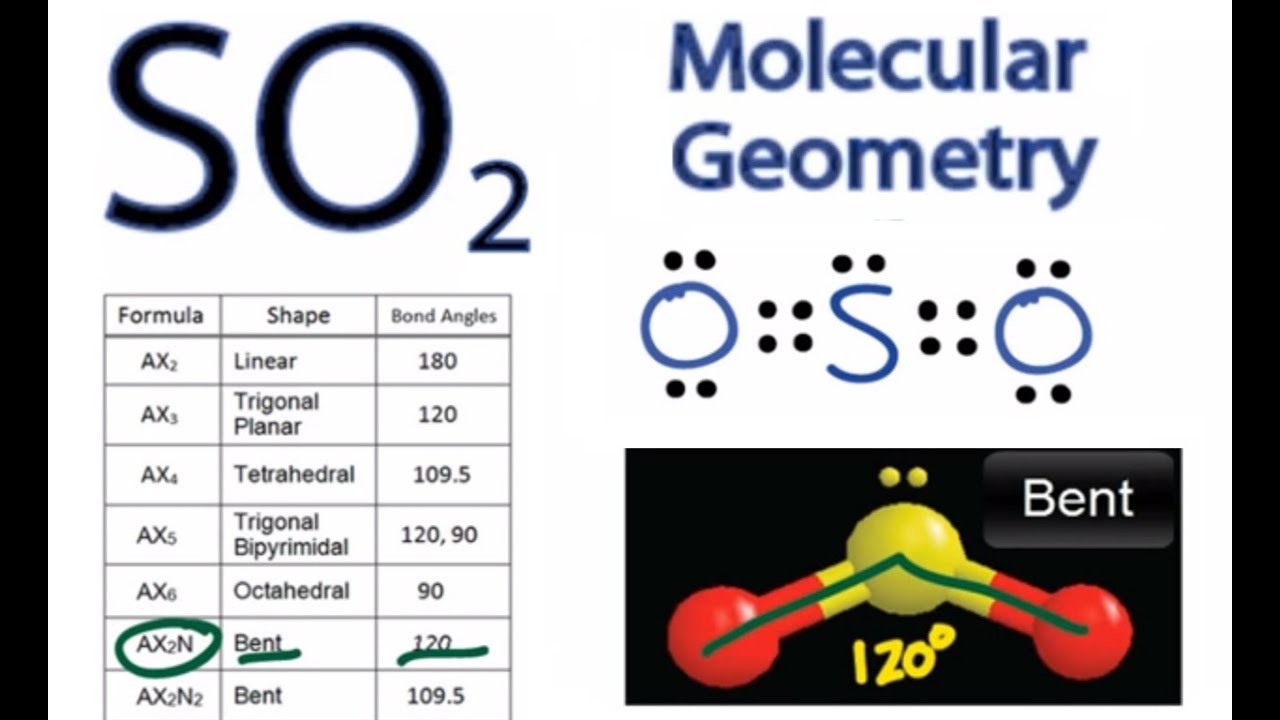
This VESPR procedure is summarized as follows: Can hydrogen atoms be a central atom (2) H. VESPR Produce to predict Molecular geometry In this case, the carbon atom is surrounded by two regions of electron density, one for each double bond it forms with the sulphur atoms. Example 1: Draw the electron dot formula and build the molecular model of water, H2O. Using this information, we can describe the molecular geometry, the arrangement of the bonded atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion. From the BP and LP interactions we can predict both the relative positions of the atoms and the angles between the bonds, called the bond angles. Each group around the central atom is designated as a bonding pair (BP) or lone (nonbonding) pair (LP). In the VSEPR model, the molecule or polyatomic ion is given an AX mE n designation, where A is the central atom, X is a bonded atom, E is a nonbonding valence electron group (usually a lone pair of electrons), and m and n are integers. The CS2 molecule has a linear geometry shape because it contains two sulfur atoms in. Molecular geometry: Molecular geometry is defined as the three dimensional arrangement of atoms that constitutes a molecule Carbon disulfide, CS2, will have a total of 16 valence electrons, 4 from the carbon atom and 6 from each of the two sulfur atoms Each of the following molecules are structurally related. Groups are placed around the central atom in a way that produces a molecular structure with the lowest energy, that is, the one that minimizes repulsions. The S-C-S bond angle is 180 degrees in the linear CS2 molecular geometry. Step 2: Determine the Central Atom of the Molecule. The molecular geometry will thus be linear, the basic #"AX"_2# model.\): Electron Geometries for Species with Two to Six Electron Groups. total valence electron number in CO32- is. Predict the geometry and polarity of the CS2 molecule. the structure of the S12 ring is closer to a perfect D3d geometry in CS2. The molecular geometry and the electron geometry are the same for CS2 C S 2 since all the valence electrons on the central carbon atom are involved in covalent. The Lewis structure reveals an unpaired electron (free radical) in which of the following species. It will use one s and one p orbitals to form the hybrids, and the remaining p-orbitals to form pi bonds with the two sulfur atoms. Table 13 Molecular structure parameters of monoclinic S13 at 173 Ka 38. The carbon atom will thus be #"sp"# hybridized. This means that its steric number will be equal to #2#. CS 2 (carbon disulfide) has one carbon atom and two sulfur atoms. The molecular geometry of CS2 is linear with symmetric electron region distribution around the central atom. In this case, the carbon atom is surrounded by two regions of electron density, one for each double bond it forms with the sulfur atoms.
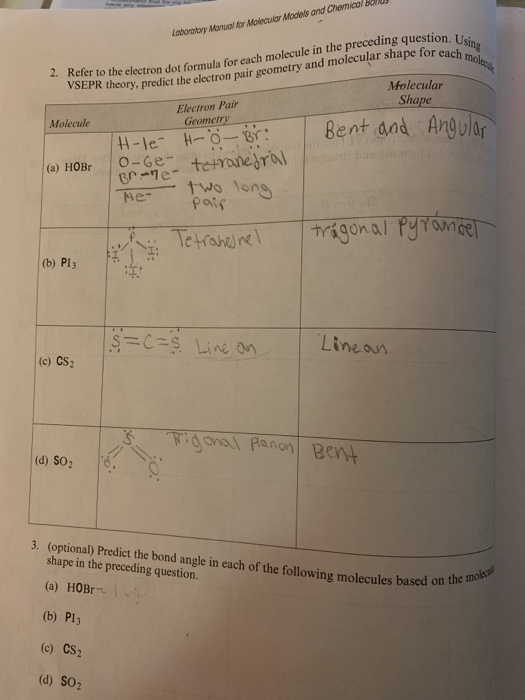
Now, molecular geometry is determined by the hybridization of the central atom. The remaining #8# valence electrons will be placed as lone pairs, two on each sulfur atom. These bonds will account for #8# of the #16# valence electrons of the molecule. The central carbon atom will form double bonds with the two sulfur atoms.

Carbon disulfide contains one carbon atom and two sulfur atoms. The best place to start when trying to figure out a molecule's geometry is its Lewis structure.Ĭarbon disulfide, #"CS"_2#, will have a total of #16# valence electrons, #4# from the carbon atom and #6# from each of the two sulfur atoms. The molecular geometry of carbon disulfide is linear because the electrons are equally distributed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
